6th
century
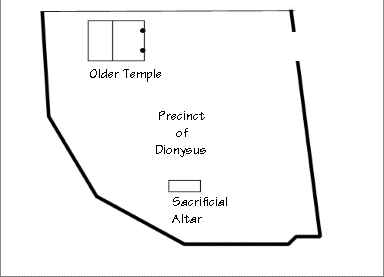
The initial part of the Dionysus’ theater, which was the first theater ever and was erected under Acropolis in Athens, (and therefore all the other Greek theaters generally) is the temple of Dionysus.

The
evolution of the Greek theater was a
gradual fact. Between the participants of the show and the viewers
there was no
curtain or any type of barrier in the orchestra.
In
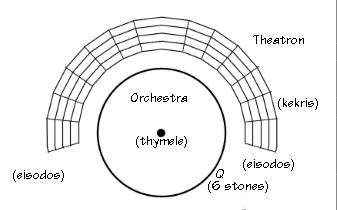
the orchestra which was made for the
dancers of the chorus was the most ancient part of the theater. At
first, the
theater of Dionysus was rectangular


and then became circular. The circular shape of the orchestra was connected with the circular dances of the early Greek folks fests.

Placed
in the middle of the orchestra
was the thymeli, an altar devoted to Dionysus.

Initially
the viewers had to stand around
the orchestra on a descending slope of the hill and later they had to
sit on
wooden benches.
The cylon - cavea (koilon), the place for the spectators (whose name was theatron at first meaning the place where someone could see) was rectangular at first.

Plenty of time passed till the cylon got its circular form which was created by digging the hill of Acropolis.
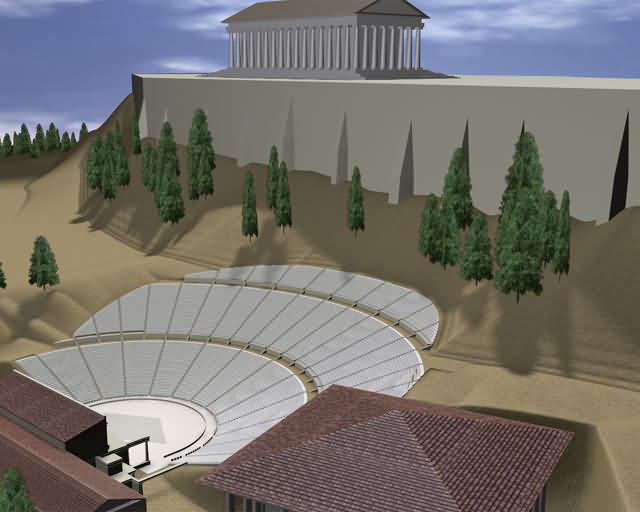

The space of the actors was the skene
(stage). In the beginning the
skene was an extemporary woodshed in the outskirt of the orchestra and
it was
used as backstage and storing and as dressing room for the actors. The
building
of the scene is separated from the orchestra and the cavea
(koilon), so as no obstruct the vista (view)
of the natural environment. Aeschylus incorporated the skene in the act
thus
the entrance and the exit of the actors from the theater was easier.
From here
and on the viewers sat semicircular. The acting
area (logion) was between the orchestra and the skene. At first it
was
totally flat but
later it was raised over the level of the
orchestra.
