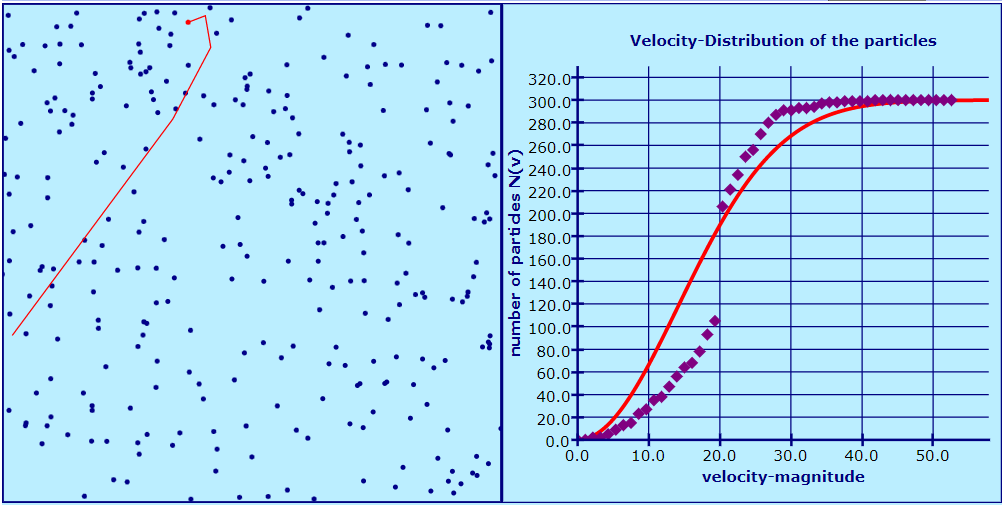
 In this work we describe the theoretical model of an ideal 2-dimensional gas. We show that the velocity distribution function of the gas varies with time and it converges to an equilibrium distribution -the Maxwell-Boltzmann one. We prove that the variation of the velocity distribution with time is caused by the mutual interactions of the particles. Then, we derive the condition satisfied by the probability density in the equilibrium state, and we formulate its analytic expression. Finally, we formulate the Boltzmann's H-theorem: we prove that the velocity distribution of the gas converges with time to the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, independently of the initial velocity distribution of the gas.
In this work we describe the theoretical model of an ideal 2-dimensional gas. We show that the velocity distribution function of the gas varies with time and it converges to an equilibrium distribution -the Maxwell-Boltzmann one. We prove that the variation of the velocity distribution with time is caused by the mutual interactions of the particles. Then, we derive the condition satisfied by the probability density in the equilibrium state, and we formulate its analytic expression. Finally, we formulate the Boltzmann's H-theorem: we prove that the velocity distribution of the gas converges with time to the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, independently of the initial velocity distribution of the gas. In the virtual environment of the simulation the user can test experimentally the Boltzmann H-theorem in the case of the 2-dimensional ideal gas. He can check in real time if the particles' velocity distribution converges with time to the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, irrespectively of the analytic form of the initial distribution.